CentOS 6 和 CentOS 7 介绍
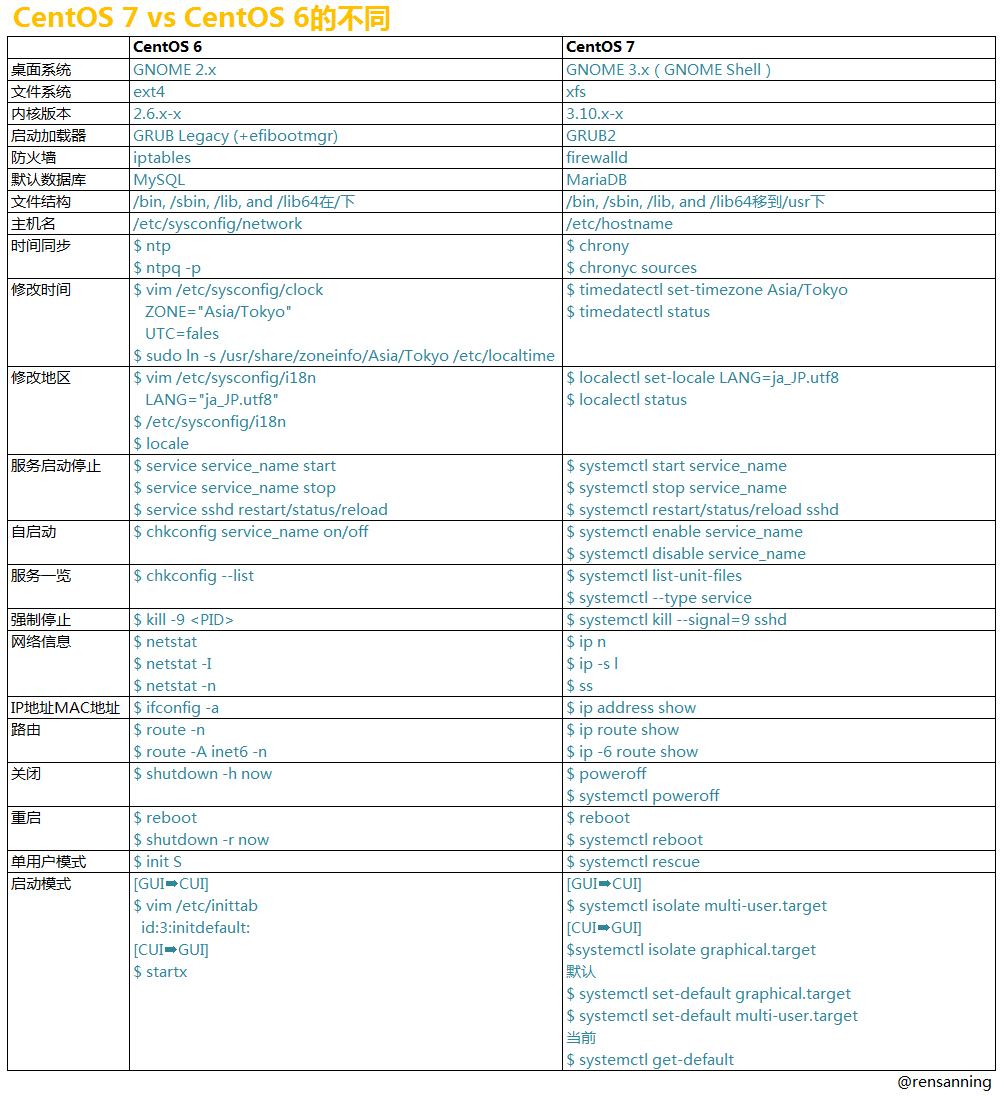
总体差异
想装回过去的一些工具
- 安装:
yum install -y tree net-tools bind-utils tree sysstat vim-en* lrzsz NetworkManager-tui ntp ntpdate iftop tcpdump telnet traceroute
查看版本号/主机名
cat /etc/redhat-releasecat /etc/hostname
常用配置差异
systemctl 的用法
- 相当于 CentOS 6 的:service nginx stop
systemctl is-enabled iptables.service #查询服务是否开机启动systemctl enable iptables.service #开机运行服务systemctl disable iptables.service #取消开机运行systemctl start iptables.service #启动服务systemctl stop iptables.service #停止服务systemctl restart iptables.service #重启服务systemctl reload iptables.service #重新加载服务配置文件systemctl status iptables.service #查询服务运行状态systemctl --failed #显示启动失败的服务systemctl list-units --type=service #查看所有服务systemctl is-enabled httpd #查看httpd服务是否开机启动- 对于启动脚本的存放位置,也不再是
/etc/init.d/(这个目录也是存在的),而是 /usr/lib/systemd/system/
开放端口
- 一般设置软件端口有一个原则:
- 0 ~ 1024 系统保留,一般不要用到
- 1024 ~ 65535(2^16) 可以随意用
- 添加单个端口:
firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=8883/tcp --permanent
- 添加范围端口:
firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=8883-8885/tcp --permanent
- 删除端口:
firewall-cmd --zone=public --remove-port=8883/tcp --permanent
- 重启防火墙:
firewall-cmd --reload
- 命令解释:
--zone #作用域--add-port=80/tcp #添加端口,格式为:端口/通讯协议--permanent #永久生效,没有此参数重启后失效
- 列出所有端口列表:
firewall-cmd --list-all
关闭 firewall 使用 iptables
- 关闭 firewall
systemctl stop firewalld.service #停止firewallsystemctl disable firewalld.service #禁止firewall开机启动
- 安装 iptables
yum install -y iptables-services
- 启动 iptables
systemctl restart iptables.service #最后重启防火墙使配置生效systemctl enable iptables.service #设置防火墙开机启动- 其他使用照旧
ifconfig 没有了
- 查看网络配置:
ip a
- 装回 ifconfig:
yum install -y net-tools
设置时区
timedatectl set-timezone Asia/Shanghaitimedatectl status
资料